Difference between revisions of "Managing Hosts with the VMM Administrator Console"
(→Adding Hosts to the VMM Administrator Console) |
m (Text replacement - "<google>BUY_VMM_BOTTOM</google>" to "<htmlet>vmm</htmlet>") |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | In the previous chapter entitled [[A Guided Tour of the VMM Administrator Console]] we took a high level tour of the VMM 2008 Administrator Console component. This chapter is intended to | + | <table border="0" cellspacing="0" width="100%"> |
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td width="20%">[[A Guided Tour of the VMM Administrator Console|Previous]]<td align="center">[[VMM 2008 Essentials|Table of Contents]]<td width="20%" align="right">[[Creating and Managing VMM 2008 Virtual Machine Templates|Next]]</td> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td width="20%">A Guided Tour of the VMM Administrator Console<td align="center"><td width="20%" align="right">Creating and Managing VMM 2008 Virtual Machine Templates</td> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <htmlet>vmm</htmlet> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In the previous chapter entitled [[A Guided Tour of the VMM Administrator Console]] we took a high level tour of the VMM 2008 Administrator Console component. This chapter is intended to cover the steps necessary to manage and monitor the hosts on which the virtual machines reside using the console. | ||
== Launching the VMM Administrator Console == | == Launching the VMM Administrator Console == | ||
| − | The VMM Administrator Console may | + | The VMM Administrator Console may be launched by selecting the ''Start->All Programs->Microsoft System Center->Virtual Machine Manager 2008->Virtual Machine Manager Administrator Console'' menu option. Given the depths to which this tool is buried in the menu structure, a shortcut on the Start menu or desktop (if one does not already exist) is recommended. |
Alternatively, the VMM Administrator Console may be started from a command prompt window by launching the VmmAdmin.exe executable. This executable is installed by default in %ProgramFiles%\Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2008\bin. | Alternatively, the VMM Administrator Console may be started from a command prompt window by launching the VmmAdmin.exe executable. This executable is installed by default in %ProgramFiles%\Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2008\bin. | ||
| − | The first time that the console is launched, a dialog will appear requesting details of the computer hosting the VMM Server to which the console is to connect | + | The first time that the console is launched, a dialog will appear requesting details of the computer hosting the VMM Server to which the console is to connect together with the port to be used in establishing this connection. This server name entry takes the following form: |
:<tt>computername:port</tt> | :<tt>computername:port</tt> | ||
| − | For example, to connect to VMM Server running a remote system named WINSERVER using port 8100, the following server information would be entered: | + | For example, to connect to a VMM Server running on a remote system named WINSERVER using port 8100, the following server information would be entered: |
:<tt>WINSERVER:8100</tt> | :<tt>WINSERVER:8100</tt> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 33: | ||
When the VMM Administrator Console is run for the first time after installation, it does not, by default, have any hosts assigned to it. In this context, the term ''host'' is used to refer to servers running virtual machines using Hyper-V, Virtual Server VMware ESX Server virtualization technology. Since very little can be achieved using the console until some hosts are added, this is one of the first tasks to be performed. | When the VMM Administrator Console is run for the first time after installation, it does not, by default, have any hosts assigned to it. In this context, the term ''host'' is used to refer to servers running virtual machines using Hyper-V, Virtual Server VMware ESX Server virtualization technology. Since very little can be achieved using the console until some hosts are added, this is one of the first tasks to be performed. | ||
| − | Hosts are added to the console using the ''Hosts'' view, which is selected by clicking on ''Hosts'' option in the list of views located in the pane in the bottom left hand corner of the console window. Once the Hosts view is displayed, hosts may be added by clicking on the ''Add Host'' link in the ''Actions'' pane, or selecting the ''Actions->Virtual Machine Manager->Add Host'' menu option. Once selected, the ''Add Hosts'' wizard will appear displaying the ''Select Host Location'' screen as illustrated in the following figure: | + | Hosts are added to the console using the ''Hosts'' view, which is selected by clicking on the ''Hosts'' option in the list of views located in the pane in the bottom left hand corner of the console window. Once the Hosts view is displayed, hosts may be added by clicking on the ''Add Host'' link in the ''Actions'' pane, or selecting the ''Actions->Virtual Machine Manager->Add Host'' menu option. Once selected, the ''Add Hosts'' wizard will appear displaying the ''Select Host Location'' screen as illustrated in the following figure: |
| Line 30: | Line 42: | ||
If a host on a perimeter network is specified, the host must have had the ''VMM Agent'' component installed on it before it can be added to the VMM Server. This installation process also involves the creation of an encryption key which will also need to be provided during the host addition process. For details on installing the VMM Agent on a perimeter host refer to the chapter entitled [[Installing VMM 2008 Components]]. | If a host on a perimeter network is specified, the host must have had the ''VMM Agent'' component installed on it before it can be added to the VMM Server. This installation process also involves the creation of an encryption key which will also need to be provided during the host addition process. For details on installing the VMM Agent on a perimeter host refer to the chapter entitled [[Installing VMM 2008 Components]]. | ||
| − | |||
After selecting the host location and type, enter the user name and password credentials of an account on the host which may be used to gain access and click ''Next'' to proceed to the ''Select Host Servers'' screen. | After selecting the host location and type, enter the user name and password credentials of an account on the host which may be used to gain access and click ''Next'' to proceed to the ''Select Host Servers'' screen. | ||
| − | Having defined the location of the hosts to be added, the purpose of the ''Select Host Servers'' screen is to allow selection of the specific hosts to be added to the VMM | + | Having defined the location of the hosts to be added, the purpose of the ''Select Host Servers'' screen is to allow selection of the specific hosts to be added to the VMM Server. To add hosts, enter the name of Active Directory domain of which the host is a member followed by the computer name. If in doubt as to the name of the computer to be added, the ''Search'' button may be used to search the specified domain for systems running either Virtual Server or Hyper-V technology. Once a list of servers has been generated, one or more hosts may be selected and added to the console. Alternatively, if you know the name of the host to be added, simply enter the name and click the ''Add'' button: |
| Line 40: | Line 51: | ||
| − | Once the required hosts have been added, click on the ''Next'' button to proceed to the ''Configuration Settings'' screen. This screen is used to define which group of hosts the machine is to be assigned to. By default, only the ''All Hosts'' group is pre-configured within the VMM Administrator Console. In addition, if the host is currently managed by a different VMM Server than the one to which the VMM Administrator Console is currently connected, select the option to ''Reassociate host with this Virtual Machine Manager Server''. | + | Once the required hosts have been added, click on the ''Next'' button to proceed to the ''Configuration Settings'' screen. This screen is used to define which group of hosts the machine is to be assigned to. By default, only the ''All Hosts'' group is pre-configured within the VMM Administrator Console. In addition, if the host is currently managed by a different VMM Server than the one to which the VMM Administrator Console is currently connected, select the option to ''Reassociate host with this Virtual Machine Manager Server'' to associate the host with the currently connected VMM Server. |
| − | Clicking ''Next'' | + | Clicking ''Next'' displays the ''Host Settings'' screen where a number of paths suitable for storing virtual machine files on the host may be defined. If no paths are specified, the default location will be used for all virtual machines created on the host using the console. Note that the console will not create any paths if they do not already exist on the host. These paths must be manually created before they can be used to store virtual machines. In addition, a remote connection port may be specified to allow remote connections to the host using the Virtual Machine Connection tool. |
| − | Once the host settings are defined, click ''Next'' | + | Once the host settings are defined, click ''Next'' and review the information on the ''Summary'' screen. In previous chapters we have mentioned that VMM 2008 sits on top of Windows PowerShell and that any operations performed are converted into a Windows PowerShell script and executed. To prove this, click on the ''View script'' button to display the PowerShell script which will be executed to add the host to the VMM Server. |
Assuming all is correct in the summary, click on ''Add hosts'' to add the hosts to the VMM Server. Once the addition is complete, the new host will appear in the list of hosts in the main console window. | Assuming all is correct in the summary, click on ''Add hosts'' to add the hosts to the VMM Server. Once the addition is complete, the new host will appear in the list of hosts in the main console window. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 61: | ||
== Configuring Host Groups == | == Configuring Host Groups == | ||
| − | In the previous section a host was added to the ''All Hosts'' group of the VMM | + | In the previous section a host was added to the ''All Hosts'' group of the VMM Server. In addition to the ''All Hosts'' group, other groups may be created and existing groups removed to aid in the administration of large and complex virtualization deployments. |
| − | + | Host groups are configured hierarchically, with the ''All Hosts'' group at the top of the tree and other sub-groups nested beneath it. Each sub-group may, in turn, have its own sub-groups allowing multiple layers of group nesting. For example, ''All Hosts'' may have a sub-group for all hosts located in California. The California sub-group may then be configured to have sub-groups of its own for each city in which hosts are located (San Jose, Palo Alto, San Francisco etc). | |
| − | To remove an existing group, right click on the group name in the Hosts pane and select ''Remove'' from the popup menu. To move a host from one group to another, select the host from the list of hosts and click on the ''Move to host group'' link in the ''Actions'' pane. Navigate through the tree of host groups to find the target group and click ''OK'' to | + | To add a new host group, ensure that the VMM Administrator Console is displaying the ''Hosts'' view, right click on the ''All Hosts'' item in the ''Hosts'' pane in the top left hand corner of the window and select ''New host group'' from the menu. A new host group entry will appear with the default name ''New host group'' highlighted. Enter a new name and press enter to complete the creation process. |
| + | |||
| + | To remove an existing group, right click on the group name in the Hosts pane and select ''Remove'' from the popup menu. To move a host from one group to another, select the host from the list of hosts and click on the ''Move to host group'' link in the ''Actions'' pane. Navigate through the tree of host groups to find the target group and click ''OK'' to initiate the move. Similarly, to add an existing host to a group, select the host group from the list, click on ''Add host'' from the Actions pane and use the wizard as described above to complete the process. | ||
== Setting Host Reserves == | == Setting Host Reserves == | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Host Reserves'' define how much of a host's resources are to be reserved for the host operating system. Once these reserves are configured, a virtual machine cannot be deployed on that host if doing so would require the use of those reserved resources. The host resources that may be reserved are as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * CPU Percentage | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Memory | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Disk Space | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Maximum Disk I/O Per Second (IOPS) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Network Capacity Percentage | ||
| + | |||
| + | Host reserves are specified on a host group basis. In addition, the group reserve settings may also be overridden on a per host basis. To specify the host group reserve settings, right click on the host group name in the Hosts pane, select ''Properties'' from the menu and click the ''Host Reserve Tabs'' in the ''Host Group Properties'' dialog as illustrated in the following figure: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:vmm_admin_console_host_group_properties.jpg|The VMM Administrator Console Host Group Properties dialog]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In order to override the group host reserve settings, right click on the host in the list, select ''Properties'' and click on ''Reserves'' in the resulting dialog. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Viewing and Configuring Host Properties == | ||
| + | |||
| + | A variety of host property categories and settings may be viewed and configured by selecting the required host from the ''Hosts'' view of the VMM Administrator Console followed by the ''Properties'' option from the Actions pane. The properties dialog presents a number of different pages of settings, each of which is accessed by clicking the corresponding tab: | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Summary === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The summary page of the host properties dialog displays general system information about the host computer. This information includes the computer name, domain information and basic information about the CPU, memory, disk space, operating system and virtualization software on the host. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Status === | ||
| + | |||
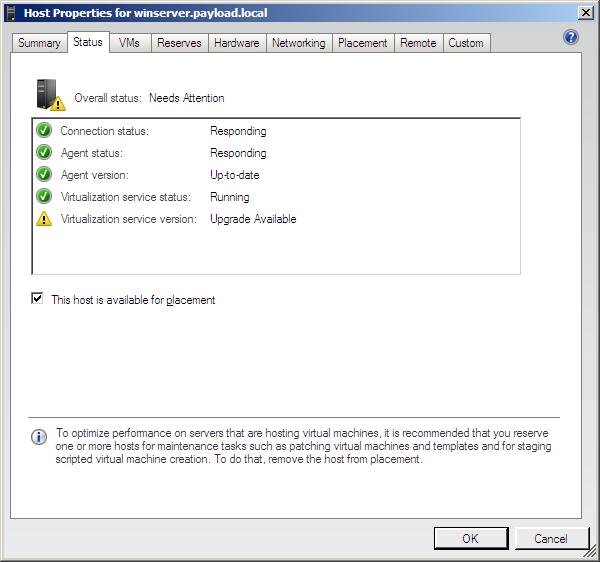
| + | Displays status information about the selected host. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:vmm_admin_console_host_status.jpg|The host properties status display]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Status information falls into the following categories: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Overall Status''' - Provides a single point for information on the status of the system. Status can be ''OK'', ''Needs attention'' meaning there is a problem which is reported in the following status fields or ''OK (Limited)'' meaning the host is a VMware Server ESX Server system and additional login information is needed to gain access to the system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Connection Status''' - Indicates whether the VMM Server component is able to communicate with the host. Options are ''Responding'', ''Not Responding'' and ''Access Denied''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Agent Status''' - Indicates whether the VMM Server component is able to communicate with the VMM Agent on the host. Options are ''Responding'', ''Not Responding'' and ''Access Denied''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Agent Version''' - Indicates whether the VMM Agent installed on the host system is the latest available version. If the host is running an older version, the status will be listed as ''Upgrade available''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Virtualization Service''' - Indicates whether the virtualization service is running on the host. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Virtualization service version''' - Indicates whether a newer version of the virtualization service is available for the host. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === VMs === | ||
| + | |||
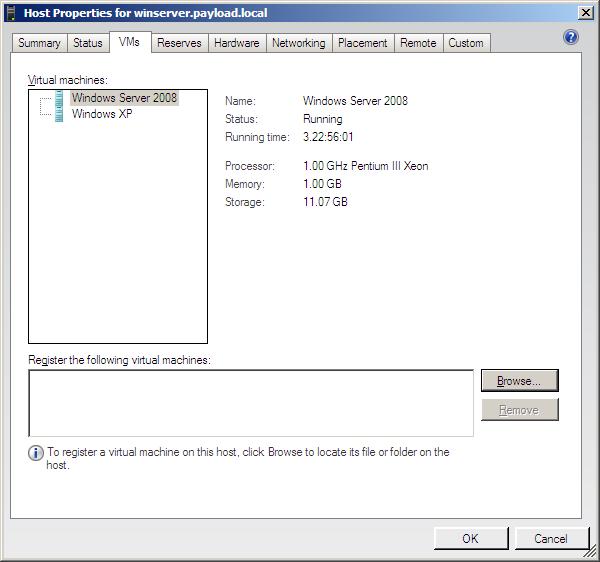
| + | The VMs screen of the VMM Administrator Console host properties dialog displays information about any virtual machines present on the selected host. Information such as the virtual machine name, status, current uptime and resources is provided for each VM on the host. In addition, virtual machines which are on the host but not yet registered with the VMM Server component may be registered by using the browse button to navigate to the location of the VM files on the host system: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[ Image:vmm_admin_console_vms.jpg|VMM Administrator Console host VM Settings]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Reserves === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Host Reserves'' define how much of a host's resources are to be reserved for the host operating system. Once these reserves are configured, a virtual machine cannot be deployed on that host if doing so would require the use of the reserved resources. The host resources that may be reserved are as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * CPU Percentage | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Memory | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Disk Space | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Maximum Disk I/O Per Second (IOPS) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Network Capacity Percentage | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Hardware === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The ''Hardware'' screen displays information about the hardware configuration of the host system. Information provided includes storage devices, CPU, network adapters and memory. Some settings may be changed such as network adapter and disk storage options. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Networking === | ||
| + | |||
| + | This screen provides the ability to view and change virtual network settings on the selected host. Each configured virtual network may be selected from the list in the left hand pane and the corresponding settings changed in the center pane. For example, an existing virtual network may be changed from a private network to an internal network. In addition, virtual networks may be added or removed using this screen. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Placement === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The term ''Placement'' refers to the paths that are available for the storage of virtual machine files on the host. As such, this screen lists the currently configured placement locations and provides the ability to add additional paths to the list of available locations and to remove any locations which are no longer to be made available. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Remote === | ||
| + | |||
| + | This page allows the port used by the Virtual Machine Remove Connection tool to connect to the virtual machines on the host to be viewed and modified. The default is 2179 for Hyper-V based hosts and 5900 for Virtual Server. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Custom === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Allows custom columns to be added to the ''Hosts'' table in the main pane of the VMM Administration Console Hosts view. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Host Network View == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The VMM Administration Console also provides the ability to view a diagram of the network configuration on the host in relation to the virtual machines. When selected, this option displays a graphical overview which includes all the virtual machines, virtual networks and physical adapters on the host together with an indication of how these are all connected. To obtain this view, select the desired host from the list of managed hosts and click on the ''View networking'' link located in the Actions pane (this option is also available by right clicking on the host and making a selection from the popup menu). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following dialog shows the networking view for a host with two virtual machines, two physical network adapters and a single internal virtual network. The two virtual machines are each connected to a physical adapter and there are currently no virtual machines configured to use the internal virtual network. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:vmm_admin_console_host_networking_view.jpg|The VMM Administration Console Host Networking View]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In addition, the information displays may be filtered by using the ''Scope'' button to define which hosts and virtual machines are to including the networking diagram. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <htmlet>vmm</htmlet> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:46, 29 May 2016
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
| A Guided Tour of the VMM Administrator Console | Creating and Managing VMM 2008 Virtual Machine Templates |
| Purchase and download the full PDF version of this VMM 2008 eBook for only $8.99 |

|
In the previous chapter entitled A Guided Tour of the VMM Administrator Console we took a high level tour of the VMM 2008 Administrator Console component. This chapter is intended to cover the steps necessary to manage and monitor the hosts on which the virtual machines reside using the console.
Launching the VMM Administrator Console
The VMM Administrator Console may be launched by selecting the Start->All Programs->Microsoft System Center->Virtual Machine Manager 2008->Virtual Machine Manager Administrator Console menu option. Given the depths to which this tool is buried in the menu structure, a shortcut on the Start menu or desktop (if one does not already exist) is recommended.
Alternatively, the VMM Administrator Console may be started from a command prompt window by launching the VmmAdmin.exe executable. This executable is installed by default in %ProgramFiles%\Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2008\bin.
The first time that the console is launched, a dialog will appear requesting details of the computer hosting the VMM Server to which the console is to connect together with the port to be used in establishing this connection. This server name entry takes the following form:
- computername:port
For example, to connect to a VMM Server running on a remote system named WINSERVER using port 8100, the following server information would be entered:
- WINSERVER:8100
To connect to the VMM Server instance running on the local system, the name localhost may be entered in place of the computer name. The option is also provided to make this selection the default for future sessions, avoiding the necessity to fill in the form on future invocations. Once an appropriate server name has been specified, the Connect button will establish the connection to the VMM Server and display the VMM Administrator Console.
Adding Hosts to the VMM Administrator Console
When the VMM Administrator Console is run for the first time after installation, it does not, by default, have any hosts assigned to it. In this context, the term host is used to refer to servers running virtual machines using Hyper-V, Virtual Server VMware ESX Server virtualization technology. Since very little can be achieved using the console until some hosts are added, this is one of the first tasks to be performed.
Hosts are added to the console using the Hosts view, which is selected by clicking on the Hosts option in the list of views located in the pane in the bottom left hand corner of the console window. Once the Hosts view is displayed, hosts may be added by clicking on the Add Host link in the Actions pane, or selecting the Actions->Virtual Machine Manager->Add Host menu option. Once selected, the Add Hosts wizard will appear displaying the Select Host Location screen as illustrated in the following figure:
The purpose of this screen is to specify where the host is located in terms of the logical network infrastructure. A variety of different host types may be added to the console, these being a Windows Server host running Hyper-V which is a member of an Active Directory domain, a Windows Server host running Hyper-V which is not a member of an Active Directory domain (also referred to as a perimeter network host), or a host running VMware ESX Server (regardless of whether or not it is an Active Directory domain member).
If a host on a perimeter network is specified, the host must have had the VMM Agent component installed on it before it can be added to the VMM Server. This installation process also involves the creation of an encryption key which will also need to be provided during the host addition process. For details on installing the VMM Agent on a perimeter host refer to the chapter entitled Installing VMM 2008 Components.
After selecting the host location and type, enter the user name and password credentials of an account on the host which may be used to gain access and click Next to proceed to the Select Host Servers screen.
Having defined the location of the hosts to be added, the purpose of the Select Host Servers screen is to allow selection of the specific hosts to be added to the VMM Server. To add hosts, enter the name of Active Directory domain of which the host is a member followed by the computer name. If in doubt as to the name of the computer to be added, the Search button may be used to search the specified domain for systems running either Virtual Server or Hyper-V technology. Once a list of servers has been generated, one or more hosts may be selected and added to the console. Alternatively, if you know the name of the host to be added, simply enter the name and click the Add button:
Once the required hosts have been added, click on the Next button to proceed to the Configuration Settings screen. This screen is used to define which group of hosts the machine is to be assigned to. By default, only the All Hosts group is pre-configured within the VMM Administrator Console. In addition, if the host is currently managed by a different VMM Server than the one to which the VMM Administrator Console is currently connected, select the option to Reassociate host with this Virtual Machine Manager Server to associate the host with the currently connected VMM Server.
Clicking Next displays the Host Settings screen where a number of paths suitable for storing virtual machine files on the host may be defined. If no paths are specified, the default location will be used for all virtual machines created on the host using the console. Note that the console will not create any paths if they do not already exist on the host. These paths must be manually created before they can be used to store virtual machines. In addition, a remote connection port may be specified to allow remote connections to the host using the Virtual Machine Connection tool.
Once the host settings are defined, click Next and review the information on the Summary screen. In previous chapters we have mentioned that VMM 2008 sits on top of Windows PowerShell and that any operations performed are converted into a Windows PowerShell script and executed. To prove this, click on the View script button to display the PowerShell script which will be executed to add the host to the VMM Server.
Assuming all is correct in the summary, click on Add hosts to add the hosts to the VMM Server. Once the addition is complete, the new host will appear in the list of hosts in the main console window.
Configuring Host Groups
In the previous section a host was added to the All Hosts group of the VMM Server. In addition to the All Hosts group, other groups may be created and existing groups removed to aid in the administration of large and complex virtualization deployments.
Host groups are configured hierarchically, with the All Hosts group at the top of the tree and other sub-groups nested beneath it. Each sub-group may, in turn, have its own sub-groups allowing multiple layers of group nesting. For example, All Hosts may have a sub-group for all hosts located in California. The California sub-group may then be configured to have sub-groups of its own for each city in which hosts are located (San Jose, Palo Alto, San Francisco etc).
To add a new host group, ensure that the VMM Administrator Console is displaying the Hosts view, right click on the All Hosts item in the Hosts pane in the top left hand corner of the window and select New host group from the menu. A new host group entry will appear with the default name New host group highlighted. Enter a new name and press enter to complete the creation process.
To remove an existing group, right click on the group name in the Hosts pane and select Remove from the popup menu. To move a host from one group to another, select the host from the list of hosts and click on the Move to host group link in the Actions pane. Navigate through the tree of host groups to find the target group and click OK to initiate the move. Similarly, to add an existing host to a group, select the host group from the list, click on Add host from the Actions pane and use the wizard as described above to complete the process.
Setting Host Reserves
Host Reserves define how much of a host's resources are to be reserved for the host operating system. Once these reserves are configured, a virtual machine cannot be deployed on that host if doing so would require the use of those reserved resources. The host resources that may be reserved are as follows:
- CPU Percentage
- Memory
- Disk Space
- Maximum Disk I/O Per Second (IOPS)
- Network Capacity Percentage
Host reserves are specified on a host group basis. In addition, the group reserve settings may also be overridden on a per host basis. To specify the host group reserve settings, right click on the host group name in the Hosts pane, select Properties from the menu and click the Host Reserve Tabs in the Host Group Properties dialog as illustrated in the following figure:
In order to override the group host reserve settings, right click on the host in the list, select Properties and click on Reserves in the resulting dialog.
Viewing and Configuring Host Properties
A variety of host property categories and settings may be viewed and configured by selecting the required host from the Hosts view of the VMM Administrator Console followed by the Properties option from the Actions pane. The properties dialog presents a number of different pages of settings, each of which is accessed by clicking the corresponding tab:
Summary
The summary page of the host properties dialog displays general system information about the host computer. This information includes the computer name, domain information and basic information about the CPU, memory, disk space, operating system and virtualization software on the host.
Status
Displays status information about the selected host.
Status information falls into the following categories:
- Overall Status - Provides a single point for information on the status of the system. Status can be OK, Needs attention meaning there is a problem which is reported in the following status fields or OK (Limited) meaning the host is a VMware Server ESX Server system and additional login information is needed to gain access to the system.
- Connection Status - Indicates whether the VMM Server component is able to communicate with the host. Options are Responding, Not Responding and Access Denied.
- Agent Status - Indicates whether the VMM Server component is able to communicate with the VMM Agent on the host. Options are Responding, Not Responding and Access Denied.
- Agent Version - Indicates whether the VMM Agent installed on the host system is the latest available version. If the host is running an older version, the status will be listed as Upgrade available.
- Virtualization Service - Indicates whether the virtualization service is running on the host.
- Virtualization service version - Indicates whether a newer version of the virtualization service is available for the host.
VMs
The VMs screen of the VMM Administrator Console host properties dialog displays information about any virtual machines present on the selected host. Information such as the virtual machine name, status, current uptime and resources is provided for each VM on the host. In addition, virtual machines which are on the host but not yet registered with the VMM Server component may be registered by using the browse button to navigate to the location of the VM files on the host system:
Reserves
Host Reserves define how much of a host's resources are to be reserved for the host operating system. Once these reserves are configured, a virtual machine cannot be deployed on that host if doing so would require the use of the reserved resources. The host resources that may be reserved are as follows:
- CPU Percentage
- Memory
- Disk Space
- Maximum Disk I/O Per Second (IOPS)
- Network Capacity Percentage
Hardware
The Hardware screen displays information about the hardware configuration of the host system. Information provided includes storage devices, CPU, network adapters and memory. Some settings may be changed such as network adapter and disk storage options.
Networking
This screen provides the ability to view and change virtual network settings on the selected host. Each configured virtual network may be selected from the list in the left hand pane and the corresponding settings changed in the center pane. For example, an existing virtual network may be changed from a private network to an internal network. In addition, virtual networks may be added or removed using this screen.
Placement
The term Placement refers to the paths that are available for the storage of virtual machine files on the host. As such, this screen lists the currently configured placement locations and provides the ability to add additional paths to the list of available locations and to remove any locations which are no longer to be made available.
Remote
This page allows the port used by the Virtual Machine Remove Connection tool to connect to the virtual machines on the host to be viewed and modified. The default is 2179 for Hyper-V based hosts and 5900 for Virtual Server.
Custom
Allows custom columns to be added to the Hosts table in the main pane of the VMM Administration Console Hosts view.
Host Network View
The VMM Administration Console also provides the ability to view a diagram of the network configuration on the host in relation to the virtual machines. When selected, this option displays a graphical overview which includes all the virtual machines, virtual networks and physical adapters on the host together with an indication of how these are all connected. To obtain this view, select the desired host from the list of managed hosts and click on the View networking link located in the Actions pane (this option is also available by right clicking on the host and making a selection from the popup menu).
The following dialog shows the networking view for a host with two virtual machines, two physical network adapters and a single internal virtual network. The two virtual machines are each connected to a physical adapter and there are currently no virtual machines configured to use the internal virtual network.
In addition, the information displays may be filtered by using the Scope button to define which hosts and virtual machines are to including the networking diagram.
| Purchase and download the full PDF version of this VMM 2008 eBook for only $8.99 |

|